Showing 1-15 of 20 results

The Fundamentals
Today on The Fundamentals, our guest Dr. Martin Myers, Director of the U-M Elizabeth Weiser Caswell Diabetes Institute, discusses diabetes research in the context of Ozempic, Wegovy, and other drugs that are changing how people think about weight loss.
You can learn more about Dr. Myers here, and you can follow the department of molecular and integrative physiology @UMPhysiology on X.

Health Lab
Researchers recently revealed a new mechanism behind antiphospholipid syndrome that the investigators hope will eventually allow treatments to be targeted closer to the source of the problem.
Health Lab
New map of the ovary provides a deeper understanding of how oocytes interact with the surrounding cells during the normal maturation process, and how the function of the follicles may break down in aging or fertility related diseases.
Health Lab
A recent U-M study uncovers a pathway utilized during normal wound healing that has the potential to reverse idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.

Health Lab
An updated rat reference provides more accuracy for research; could help researchers using rat models for the study of DNA, RNA, evolution, or genes linked to disease risks
Health Lab
A new collaborative study, examined the interaction between three naturally occurring gases — nitric oxide (NO), oxygen, and H2S — during generation of new blood vessels, called angiogenesis.

Health Lab
New study has identified an enzyme contributing to systemic sclerosis.
Health Lab
A new study links two autism-associated genes together for the first time, potentially revealing a mechanism behind brain changes seen in people with autism.

Health Lab
When it comes to lupus care, Black adults are normally left behind despite being one of the highest lupus populations.
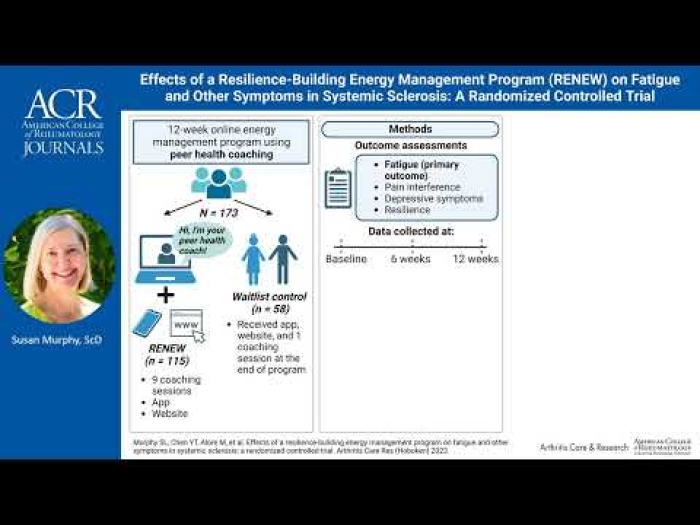
Health Lab
Research published in the Arthritis Care and Research Journal from Michigan Medicine found that scleroderma patients made significant strides when working with trained peer health coaches in adhering to wellness routines, leading to resilience and improvements in fatigue, pain and depressive symptoms.

Health Lab
Michigan Medicine researchers are examining whether ginger supplements could help treat symptoms in autoimmune diseases

Health Lab
A study in PNAS identifies a protein that, when missing, makes exercising in the cold that much harder—that is, at least in fruit flies.

Health Lab
Research from the Department of Molecular & Integrative Physiology at Michigan Medicine identifies a previously unknown genetic mutation that causes the disease called primary aldosteronism in certain populations.

Health Lab
One of the most important protein complexes in mammals involved in ERAD is called SEL1L-HRD1. Recent research finds that this protein complex helps regulate another critical protein involved in innate immunity, called STING, at the endoplasmic reticulum.

Health Lab
A Michigan Medicine study provides early evidence of a surge of activity correlated with consciousness in the dying brain.